Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a revolutionary approach in the construction industry that involves creating a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM integrates various aspects of a project, including geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, and properties of building components.
This comprehensive digital model serves as a shared knowledge resource for all stakeholders involved in the project. BIM offers numerous advantages of BIM over conventional construction methods, enabling improved collaboration, enhanced project visualization, cost and time savings, reduced errors, and efficient facility management. Let's explore these building information modeling benefits in detail.
In the planning phase, project requirements and objectives are defined. This includes establishing the project scope, setting goals and understanding the contractor’s requirements and deliverables plan.
BIM is used to create a digital representation of the project, allowing stakeholders to visualize and analyze different design options, evaluate the feasibility, and estimate costs.
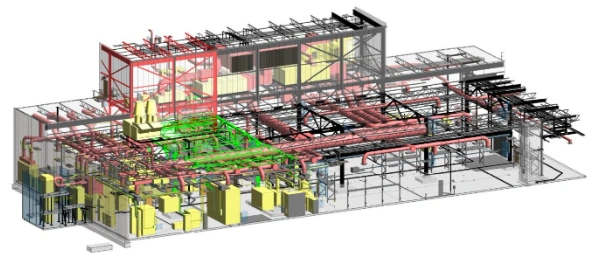
In the design phase, the project takes shape through the creation of detailed models and drawings. BIM tools are used to develop a comprehensive digital model that includes architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems. Collaboration among different disciplines is facilitated, and potential clashes or conflicts are identified and resolved within the digital environment.
During the construction phase, BIM serves as a reference for project execution. The digital model helps in coordinating construction activities, managing resources, and monitoring progress. BIM can be utilized for construction sequencing, scheduling, and tracking material quantities. On-site teams can access the model through mobile devices, ensuring they have up-to-date project information.
After construction is complete, BIM continues to play a role in the operation and maintenance of the facility. The digital model serves as a repository of information about the building's components, systems, and maintenance requirements. BIM can assist in facility management tasks, such as space management, asset tracking, and energy analysis. It supports ongoing maintenance and renovations by providing accurate and up-to-date information about the building.
BIM benefits energy efficiency evaluation by integrating energy data into the model for accurate simulations. It helps optimize building energy performance, identify improvements, and evaluate energy-efficient design alternatives. BIM's data integration enables seamless information exchange with energy analysis software, improving evaluation accuracy and efficiency. Centralized project data ensures up-to-date energy information for ongoing monitoring and management.
A growing trend in the AEC industry is involving estimators during the early planning phase for better construction cost estimation. This has led to the rise of model-based cost estimating, also known as 5D BIM. By utilizing BIM tools like Autodesk's Revit and BIM 360 Docs, the process of quantifying and applying costs is automated, freeing up estimators to concentrate on more valuable tasks such as identifying construction assemblies and assessing risks.
BIM enables comprehensive project planning and visualization before construction, providing a clear understanding of the project before any physical work begins. Through space-use simulations and 3D visualizations, clients can experience and make adjustments to the space, avoiding costly modifications during construction. It's like having a better view from the beginning to prevent costly changes later.
Digital BIM models enable efficient sharing, collaboration, and versioning compared to paper drawings. Tools like Autodesk's BIM 360 facilitate seamless collaboration among project disciplines, ensuring all stakeholders have project insight. Cloud-based access enables on-site review of drawings and models through mobile devices, providing up-to-date project information. The BIM 360 ecosystem empowers teams to share models, coordinate planning, and access project data anytime.
BIM helps coordinate different trades and subcontractors by identifying clashes early on, such as conflicts between electrical conduits and steel beams or insufficient doorway inter-trade clash identification & coordination.
Autodesk's BIM 360 Glue automates clash detection, preventing rework on construction projects. By planning accurately with BIM, you can minimize last-minute changes and unexpected problems. Easy reviewing and commenting across multiple disciplines further enhance project coordination.
BIM offers significant benefits in data integration for construction projects. It centralizes project data, enhances collaboration, and reduces data silos. BIM supports interoperability, enabling the integration of data from various sources. It provides real-time updates, ensuring stakeholders have access to the latest information. Additionally, BIM enables advanced analysis and data-driven insights for improved decision-making and optimized project outcomes. Meta Description - BIM stands for Building Information Modelling. BIM is a process for creating and managing information on a construction project throughout its whole life cycle.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a process for creating and managing digital models of buildings. It supports collaboration and improves project outcomes. Revit, on the other hand, is a software tool used to implement BIM. It provides features for creating detailed, data-rich building models that support the BIM process.
3D CAD modeling creates visual representations of buildings, focusing on appearance. BIM (Building Information Modeling) goes further by integrating detailed data about building components and their interactions. BIM captures both visual and functional information, enhancing project accuracy and efficiency.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) offers several advantages over traditional CAD (Computer-Aided Design). BIM centralizes all project information, facilitating better collaboration and data management. Unlike CAD, which often has fragmented data, BIM integrates all project details into a single model, improving accessibility and coordination.